
The result is that the RCEP makes it much easier for Asian firms to send goods around 15 of Asia's economies, allowing for more regionally integrated supply chains. By harmonizing rules of origin from existing trade agreements among members, RCEP reduces regulatory barriers and allows for greater trade in intermediate inputs. They are designed to ensure that traded goods that get benefits are mostly, or at least partly made in a member country, rather than being trans-shipped from a country that does not get trade agreement benefits. Rules of origin are a standard part of any trade agreement. Specifically, RCEP creates standard rules of origin. While many RCEP members had existing trade agreements, the ways that RCEP “staples together” those agreements have significant economic implications. In the long term, the agreement has the potential to influence international competition and future trade rules. If RCEP is similar to other ASEAN agreements, the current provisions will likely improve over time. The projected economic benefits of RCEP are more significant than those of CPTPP ( PDF), and there are several components of RCEP that will influence the organization of supply chains in the short term. While RCEP may not be a revolutionary trade agreement, it should not be regarded as a purely symbolic agreement either. In the long term, the RCEP agreement has the potential to influence international competition and future trade rules. Overall, the agreement is projected to increase GDP in member countries by 0.2% by 2030 ( PDF), which is a little more than the projected income gains due to CPTPP. The agreement also has relatively patchy coverage on important issues like service trade and agricultural trade (although there is more coverage on agricultural goods than initially expected). RCEP will eliminate tariffs on 90% of goods, but existing trade agreements among member countries already cover roughly 80% of these goods. RCEPs tariff cuts are indeed relatively modest. This view stems from the comparison of RCEP with CPTPP, which was touted as the “gold standard” in trade agreements. Some argue that RCEP is a “shallow” agreement in terms of tariff cuts and lacks substance on 21st-century trade issues like consumer protection and labor standards. The reception of RCEP has not been entirely positive. RCEP effectively consolidates the “Asian market” in ways that previous agreements, including the CPTPP (the Trans-Pacific Partnership's successor), have not.

The United States was a party to a broad Pacific Trade deal called the Trans-Pacific Partnership but withdrew, and the remaining 11 members stayed together to form the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP). RCEP would also become the world's largest export supplier and second-largest import destination (Figure 2).

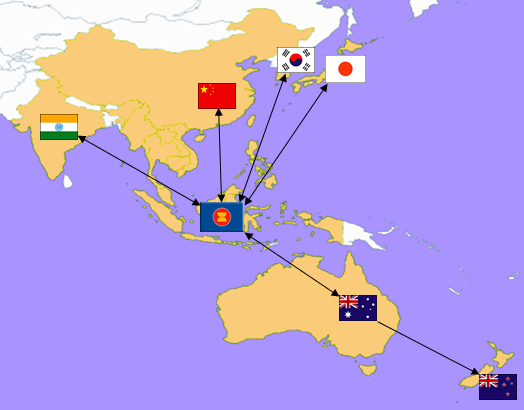
The countries involved in the agreement accounted for nearly 30% of global GDP in 2019, topping NAFTA as the world's largest trade bloc (Figure 1). Why have some heralded RCEP as a landmark agreement? For starters, any trade agreement more than eight years in the making that brings together leaders from 15 members over 28 rounds of formal negotiation could be considered monumental. The formation of RCEP highlights the multilateral approach to trade rules in Asia and creates a bright contrast to the United States' current largely unilateral and bilateral approach to trade relationships. The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) was eight years in the making and includes the 10 nations of the ASEAN, Australia, Japan, New Zealand, South Korea, and China.
#REGIONAL TRADE BLOCS FREE#
Last month, fifteen nations signed a free trade agreement of economic and political significance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
